






From The Atlantic Monthly:
Police Have a Much Bigger Domestic-Abuse Problem Than the NFL Does
Research suggests that family violence is two to four times higher in the law-enforcement community than in the general population. So where's the public outrage?

While I have no particular objection to a suspension of any length for such players, the public focus on NFL policy seems strange and misplaced to me. Despite my general preference for reducing the prison population, an extremely strong person rendering a much smaller, weaker person unconscious with his fists, as Rice did, is a situation where prison is particularly appropriate. More generally, clear evidence of domestic abuse is something that ought to result in legal sanction. Employers aren't a good stand in for prosecutors, juries, and judges.
Should ex-convicts who abused their partners be denied employment forever? I think not. Our notion should be that they've paid their debt to society in prison. Pressure on the NFL to take a harder line against domestic abuse comes in the context of a society where the crime isn't adequately punished, so I totally understand it. Observing anti-NFL rhetoric, you'd nevertheless get the impression that other employers monitor and sanction domestic abuse incidents by employees. While I have nothing against pressuring the NFL to go beyond what the typical employer does, I fear that vilifying the league has the effect of misleading the public into a belief that it is out of step with general norms on this issue. Domestic violence is less common among NFL players than the general population.
And there is another American profession that has a significantly more alarming problem with domestic abuse. I'd urge everyone who believes in zero tolerance for NFL employees caught beating their wives or girlfriends to direct as much attention—or ideally, even more attention—at police officers who assault their partners. Several studies have found that the romantic partners of police officers suffer domestic abuse at rates significantly higher than the general population. And while all partner abuse is unacceptable, it is especially problematic when domestic abusers are literally the people that battered and abused women are supposed to call for help.
If there's any job that domestic abuse should disqualify a person from holding, isn't it the one job that gives you a lethal weapon, trains you to stalk people without their noticing, and relies on your judgment and discretion to protect the abused against domestic abusers?
There's the recently retired 30-year veteran police officer who shot his wife and then himself in Colorado Springs earlier this summer. There's Tacoma Police Chief David Brame, who perpetrated another murder-suicide in April. (Update: it's in fact the tenth anniversary of this crime, which I missed in the ABC story.) Also in April, an Indiana news station reported on "Sgt. Ryan Anders, a narcotics officer," who "broke into his ex-wife's home and fatally shot her. He then turned the gun on himself." In February, "Dallas police confirmed ... that a Crandall police officer shot and killed his wife before killing himself." Last year, a Nevada police officer killed his wife, his son, and then himself. And Joshua Boren, a Utah police officer, "killed his wife, their two children, his mother-in-law and then himself" after receiving "text messages ... hours earlier threatening to leave him and take their kids and confronting him for raping her." That isn't an exhaustive survey, just a quick roundup of recent stories gleaned from the first couple pages of Google results. And statistics about "blue" domestic abuse are shocking in their own way.
As the National Center for Women and Policing noted in a heavily footnoted information sheet, "Two studies have found that at least 40 percent of police officer families experience domestic violence, in contrast to 10 percent of families in the general population. A third study of older and more experienced officers found a rate of 24 percent, indicating that domestic violence is two to four times more common among police families than American families in general." Cops "typically handle cases of police family violence informally, often without an official report, investigation, or even check of the victim's safety," the summary continues. "This 'informal' method is often in direct contradiction to legislative mandates and departmental policies regarding the appropriate response to domestic violence crimes." Finally, "even officers who are found guilty of domestic violence are unlikely to be fired, arrested, or referred for prosecution."
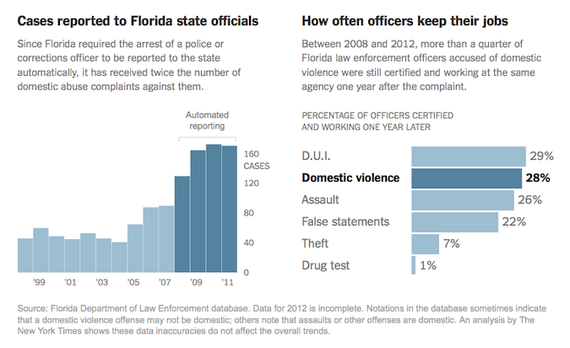
In some instances, researchers have resorted to asking officers to confess how often they had committed abuse. One such study, published in 2000, said one in 10 officers at seven police agencies admitted that they had “slapped, punched or otherwise injured” a spouse or domestic partner. A broader view emerges in Florida, which has one of the nation’s most robust open records laws. An analysis by The Times of more than 29,000 credible complaints of misconduct against police and corrections officers there strongly suggests that domestic abuse had been underreported to the state for years.A chart that followed crystallized the lax punishments meted out to domestic abusers. Said the text, "Cases reported to the state are the most serious ones—usually resulting in arrests. Even so, nearly 30 percent of the officers accused of domestic violence were still working in the same agency a year later, compared with 1 percent of those who failed drug tests and 7 percent of those accused of theft."
After reporting requirements were tightened in 2007, requiring fingerprints of arrested officers to be automatically reported to the agency that licenses them, the number of domestic abuse cases more than doubled—from 293 in the previous five years to 775 over the next five. The analysis also found that complaints of domestic violence lead to job loss less often than most other accusations of misconduct.
ADVERTISEMENT BY SMIRNOFF
Smirnoff: Quality Vodka
Our partnership with Ted Danson is a match made in heaven. It only makes sense that America’s #1 brand in vodka is partnering with America's #1 celebrity. Or at least that’s w...
It would be wonderful if domestic violence by police officers was tracked in a way that permitted me to link something more comprehensive and precise than the National Center for Women and Policing fact sheet, the studies on which it is based, the New York Times analysis, or other press reports from particular police departments. But the law enforcement community hasn't seen fit to track these cases consistently or rigorously. Says the International Association of Chiefs of Police in a 2003 white paper on the subject, "the rate of domestic violence is estimated to be at least as common as that of the general population and limited research to date indicates the possibility of higher incidence of domestic violence among law enforcement professionals." Their position on the evidence: "The problem exists at some serious level and deserves careful attention regardless of estimated occurrences."
Here's what they found:
The cases involved the arrest of 281 officers employed by 226 police agencies. Most of the cases involved a male officer (96 percent) employed in a patrol or other street-level function (86.7 percent). There were 43 supervisory officers arrested for an OIDV-related offense. One-third of the OIDV victims were the current spouse of the arrested officer. Close to one-fourth of the victims were children, including a child or a stepchild of the officer or children who were unrelated to the arrested officer. There were 16 victims who also were police officers. Simple assault was the most serious offense charged in roughly 40 percent of the cases, followed by aggravated assault (20.1 percent), forcible rape (9.9 percent), intimidation (7.1 percent), murder/non-negligent manslaughter (4.6 percent), and forcible fondling (3.7 percent).Think about that. Domestic abuse is underreported. Police officers are given the benefit of the doubt by colleagues in borderline cases. Yet even among police officers who were charged, arrested, and convicted of abuse, more than half kept their jobs.
Data on final organizational outcomes were available for 233 of the cases. About one-third of those cases involved officers who were separated from their jobs either through resignation or termination. The majority of cases in which the final employment outcome was known resulted in a suspension without job separation (n = 152). Of those cases where there was a conviction on at least one offense charged, officers are known to have lost their jobs through either termination or resignation in less than half of those cases (n = 52). More than one-fifth of the OIDV cases involved an officer who had also been named individually as a party defendant in at least one federal court civil action for depravation of civil rights under color of law pursuant to 42 U.S.C. §1983 at some point during their law enforcement careers.
Evidence of domestic-abuse problems in police departments around the U.S. is overwhelming.
The context for these incidents is a police department with a long history of police officers who beat their partners. Los Angeles Magazine covered the story in 1997. A whistleblower went to jail in 2003 when he leaked personnel files showing the scope of abuse in the department. "Kids were being beaten. Women were being beaten and raped. Their organs were ruptured. Bones were broken," he told L.A. Weekly. "It was hard cold-fisted brutality by police officers, and nothing was being done to protect their family members. And I couldn’t stand by and do nothing.”Subsequently, Ms. Magazine reported, a "review of 227 domestic violence cases involving LAPD officers confirmed that these cases were being severely mishandled, according to the LAPD Inspector-General. In more than 75 percent of confirmed cases, the personnel file omitted or downplayed the domestic abuse. Of those accused of domestic violence, 29 percent were later promoted and 30 percent were repeat offenders. The review and the revelation led to significant reforms in the LAPD's handling on police officer-involved domestic violence."
The woman called 911, seeking help from police after reportedly being assaulted by her boyfriend. But while police responded to the domestic violence call, one of the officers allegedly took the woman into an upstairs bedroom and sexually assaulted her, authorities said.Here is a case that The San Jose Mercury News reported the same month:
Officer Geoffrey Graves, 38, who has been with the Police Department for six years, was charged by Santa Clara County prosecutors with forcible rape in connection with a Sept. 22 incident. The incident began when Graves and three other San Jose officers responded to a family disturbance involving a married couple about 2 a.m., prosecutors said. The officers determined that both spouses had been drinking and had argued, but that no crime had occurred, authorities said.Then he allegedly raped her.
The woman, who works as a hotel maid, told officers that she wanted to spend the night at a hotel where she had previously worked. About 2:30 a.m., Graves drove the woman to the hotel, where she went to her room alone and fell asleep, authorities said. Fifteen minutes later, the woman heard knocking and opened the door.
There is no more damaging perpetrator of domestic violence than a police officer, who harms his partner as profoundly as any abuser, and is then particularly ill-suited to helping victims of abuse in a culture where they are often afraid of coming forward. The evidence of a domestic-abuse problem in police departments around the United States is overwhelming. The situation is significantly bigger than what the NFL faces, orders of magnitude more damaging to society, and yet far less known to the public, which hasn't demanded changes. What do police in your city or town do when a colleague is caught abusing their partner? That's a question citizens everywhere should investigate.




No comments:
Post a Comment